- English
- French
- German
- Portuguese
- Spanish
- Russian
- Japanese
- Korean
- Arabic
- Greek
- German
- Turkish
- Italian
- Danish
- Romanian
- Indonesian
- Czech
- Afrikaans
- Swedish
- Polish
- Basque
- Catalan
- Esperanto
- Hindi
- Lao
- Albanian
- Amharic
- Armenian
- Azerbaijani
- Belarusian
- Bengali
- Bosnian
- Bulgarian
- Cebuano
- Chichewa
- Corsican
- Croatian
- Dutch
- Estonian
- Filipino
- Finnish
- Frisian
- Galician
- Georgian
- Gujarati
- Haitian
- Hausa
- Hawaiian
- Hebrew
- Hmong
- Hungarian
- Icelandic
- Igbo
- Javanese
- Kannada
- Kazakh
- Khmer
- Kurdish
- Kyrgyz
- Latin
- Latvian
- Lithuanian
- Luxembou..
- Macedonian
- Malagasy
- Malay
- Malayalam
- Maltese
- Maori
- Marathi
- Mongolian
- Burmese
- Nepali
- Norwegian
- Pashto
- Persian
- Punjabi
- Serbian
- Sesotho
- Sinhala
- Slovak
- Slovenian
- Somali
- Samoan
- Scots Gaelic
- Shona
- Sindhi
- Sundanese
- Swahili
- Tajik
- Tamil
- Telugu
- Thai
- Ukrainian
- Urdu
- Uzbek
- Vietnamese
- Welsh
- Xhosa
- Yiddish
- Yoruba
- Zulu
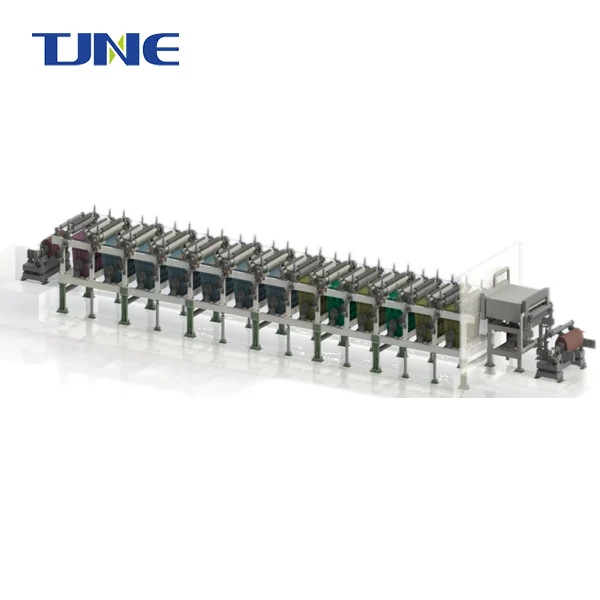
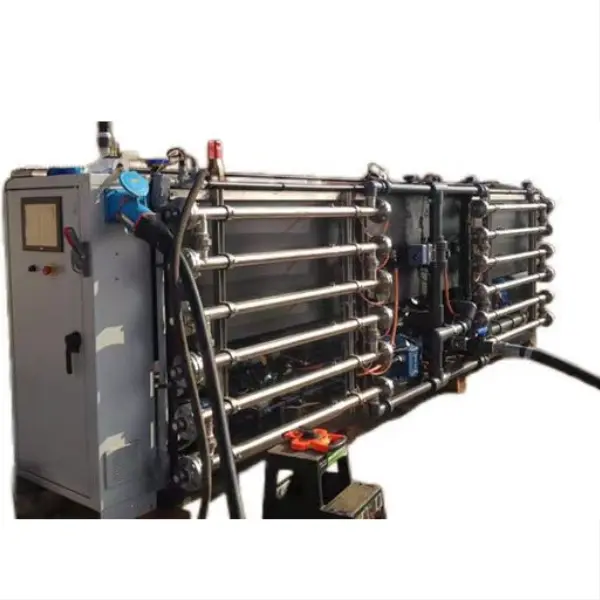
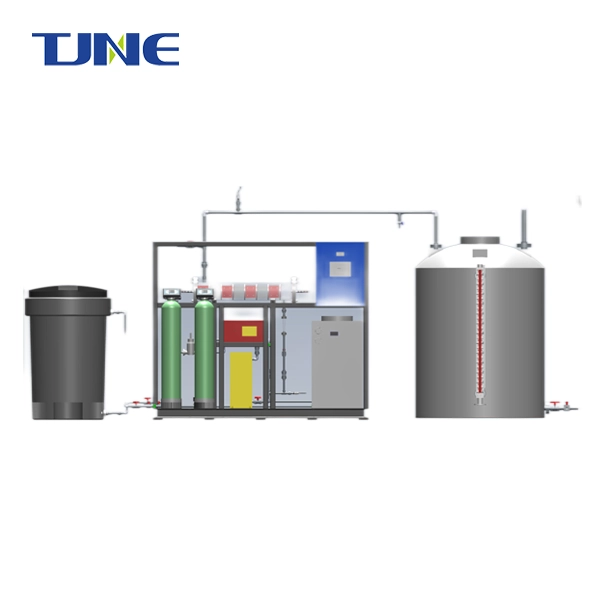
A chlorine generator electrolyzer, also known as a salt chlorinator or salt water chlorinator, is a device used in swimming pools and water treatment systems to produce sodium hypochlorite through electrolysis. This innovative technology has revolutionized pool maintenance by providing a more efficient and environmentally friendly method of water disinfection. By using salt and electricity, these systems generate sodium hypochlorite on-site, eliminating the need for manual addition of chlorine chemicals and reducing overall maintenance costs.
How does a salt water chlorinator work in a swimming pool?
Salt water chlorinators have become increasingly popular in swimming pool maintenance due to their efficiency and ease of use. These systems work by converting dissolved salt in the pool water into chlorine through a process called electrolysis. Here's a detailed breakdown of how a salt water chlorinator operates in a swimming pool:
- Salt Addition: The process begins by adding salt to the pool water. The required salt concentration is typically around 3,000 to 4,000 parts per million (ppm), which is much lower than seawater (about 35,000 ppm). This low salt level ensures that the water doesn't taste salty or feel uncomfortable to swimmers.
- Water Circulation: The pool's pump circulates the saltwater through the filtration system and the chlorine generator cell.
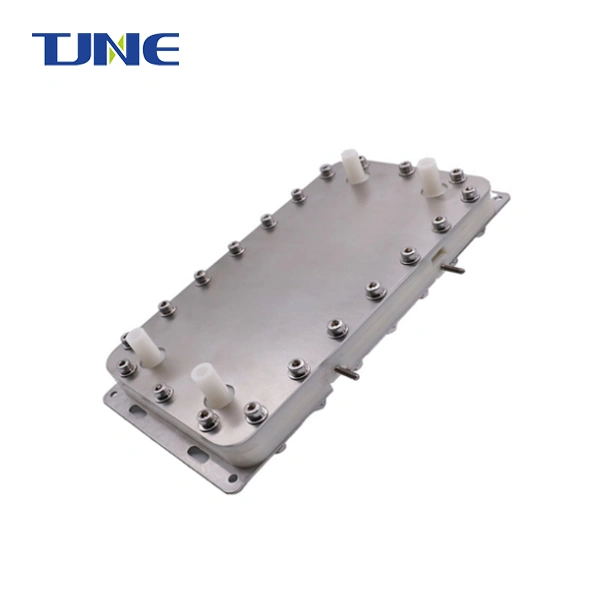
- Electrolysis Process: As the saltwater passes through the chlorinator cell, an electric current is applied to the metal plates inside. This triggers the electrolysis process, which separates the salt (sodium chloride) molecules into their component parts: sodium and chlorine.
- Chlorine Generation: The chlorine gas produced during electrolysis immediately dissolves into the water, forming sodium hypochlorite (NaCl)and hypochlorite ions (OCl-). These are the same active sanitizing agents found in traditional chlorine products.
- Sanitization: The newly formed chlorine compounds circulate back into the pool, disinfecting the water by killing bacteria, algae, and other harmful microorganisms.
- Continuous Cycle: After the chlorine has done its job, it reverts back to salt, and the process begins again. This creates a continuous cycle of chlorine production and sanitization.
- pH Balance: Most salt chlorinator systems include a pH control feature to maintain optimal water balance. This is crucial because the electrolysis process tends to increase water pH over time.
The benefits of using a salt water chlorinator in a swimming pool are numerous. Firstly, it provides a consistent level of chlorine, avoiding the peaks and valleys often associated with manual chlorine addition. This results in better water quality and a more comfortable swimming experience. Secondly, it reduces the need for storing and handling harsh chemicals, making pool maintenance safer and more convenient. Lastly, many swimmers report that salt water pools are gentler on the skin and eyes compared to traditionally chlorinated pools.
However, it's important to note that salt water chlorinators do require some maintenance. The chlorinator cell needs to be cleaned periodically to remove calcium scale buildup, and the salt levels must be monitored and adjusted as needed. Additionally, while the initial cost of installing a salt water chlorinator can be higher than traditional chlorine systems, many pool owners find that the long-term savings in chemical costs and reduced maintenance make it a worthwhile investment.
What are the advantages and disadvantages of using a chlorine generator electrolyzer?
The use of chlorine generator electrolyzers in water treatment has both advantages and disadvantages. Understanding these can help pool owners and water treatment professionals make informed decisions about implementing this technology.
Advantages:
1. Continuous Chlorine Production: One of the primary benefits of chlorine generator electrolyzers is their ability to produce sodium hypochlorite on-demand. This ensures a consistent supply of sanitizing agents in the water, maintaining better water quality and reducing the risk of bacterial growth.
2. Reduced Chemical Handling: By generating sodium hypochlorite on-site, these systems eliminate the need for storing and handling potentially dangerous chlorine chemicals. This not only improves safety but also reduces the environmental impact associated with chemical transportation and packaging.
3. Cost-Effective in the Long Run: While the initial investment may be higher, chlorine generator electrolyzers can lead to significant savings over time. The reduced need for purchasing and storing chlorine chemicals, coupled with lower maintenance requirements, can result in decreased operational costs.
4. Improved Water Quality: Many users report that water treated with a chlorine generator electrolyzer feels softer and is less likely to cause skin and eye irritation compared to traditionally chlorinated water. This is partly due to the consistent chlorine levels and the absence of chlorine by-products often found in manually chlorinated systems.
5. Environmentally Friendly: These systems reduce the carbon footprint associated with the production, packaging, and transportation of chlorine chemicals. Additionally, they produce fewer chloramine by-products, which are known to be harmful to the environment.
6. Automation and Ease of Use: Modern chlorine generator electrolyzers often come with advanced control systems that automate the chlorination process. This reduces the need for constant monitoring and manual adjustments, making water treatment more convenient and less time-consuming.
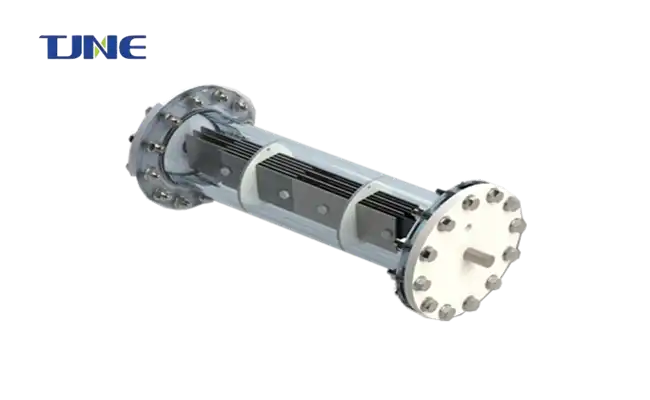

7. Versatility: These systems can be used in various applications beyond swimming pools, including water treatment plants, industrial processes, and even for on-site disinfection in remote areas.
Disadvantages:
1. High Initial Cost: The upfront investment for a chlorine generator electrolyzer system can be substantial, which may be a barrier for some potential users. This includes not only the cost of the equipment but also installation expenses.
2. Electricity Consumption: These systems require a constant supply of electricity to operate. In areas with high electricity costs, this could potentially offset some of the savings gained from reduced chemical usage.
3. Salt Addition: The need to add salt to the water may be a concern for some applications. While the salt levels are generally low, it could be an issue in areas with strict regulations on salt discharge or for individuals on low-sodium diets.
4. Potential for Corrosion: The presence of salt in the water can accelerate corrosion of metal components in and around the treated water. This is particularly relevant for swimming pools with metal ladders, handrails, or other accessories.
5. Maintenance Requirements: While generally lower than traditional chlorination methods, chlorine generator electrolyzers still require some maintenance. The electrodes need periodic cleaning to remove scale buildup, and the salt levels must be monitored and adjusted as needed.
6. Temperature Sensitivity: The efficiency of chlorine production can be affected by water temperature. In colder climates or during winter months, additional measures may be needed to maintain optimal chlorine levels.
7. Not Suitable for All Applications: While versatile, chlorine generator electrolyzers may not be appropriate for all water treatment scenarios. Some industrial processes or specialized applications may require alternative disinfection methods.
8. Potential for Overchlorination: If not properly monitored and controlled, these systems can lead to overchlorination, which can be harmful to swimmers and equipment.
In conclusion, while chlorine generator electrolyzers offer numerous benefits in terms of water quality, safety, and long-term cost-effectiveness, they also come with certain drawbacks that need to be considered. The decision to implement this technology should be based on a careful evaluation of the specific needs, regulatory requirements, and environmental conditions of each application.
How much does it cost to install and maintain a chlorine generator electrolyzer system?
The cost of installing and maintaining a chlorine generator electrolyzer system can vary widely depending on several factors, including the size of the application, the specific model chosen, and local market conditions. Understanding these costs is crucial for anyone considering implementing this technology, whether for a residential swimming pool or a larger commercial water treatment facility.
Installation Costs:
The initial installation cost of a chlorine generator electrolyzer system typically cost less for a residential swimming pool. This includes the cost of the chlorinator unit itself, depending on the size and features. Installation costs, which may include labor, additional plumbing, and electrical work.
For larger commercial or industrial applications, the costs can be significantly higher. A system for a large public pool or a small water treatment plant might cost higher, depending on the capacity and complexity of the installation.
Factors affecting installation costs include:
1. Size of the water body or flow rate to be treated
2. Existing plumbing and electrical infrastructure
3. Local labor rates
4. Brand and model of the chlorinator chosen
5. Additional features such as pH control or automation systems
It's important to note that while the upfront costs may seem high, many users find that the long-term savings in chemical costs and reduced maintenance make chlorine generator electrolyzers a cost-effective solution over time.
Maintenance Costs:
The ongoing maintenance costs for a chlorine generator electrolyzer system are generally lower than those for traditional chlorination methods. However, there are still some expenses to consider:
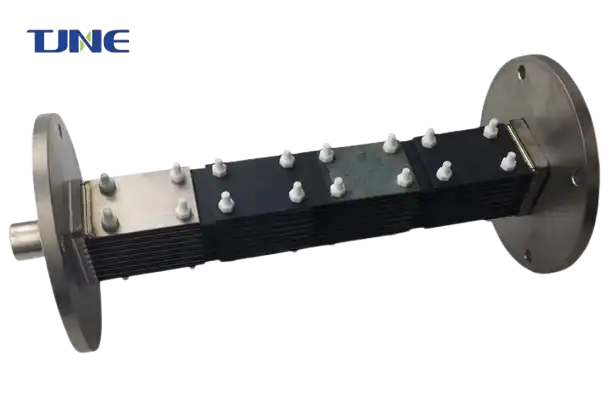

1. Salt Replenishment: The system requires a constant level of salt in the water. For a typical residential pool, you might need to add 500-1000 pounds of salt initially. After that, you'll only need to top up occasionally, usually costing less than $100 per year.
2. Electricity Consumption: The system uses electricity to power the electrolysis process. For a residential pool, this might add monthly electricity during the swimming season.
3. Cell Cleaning: The chlorinator cell needs to be cleaned periodically to remove calcium scale buildup. This can usually be done with a mild acid solution and doesn't require professional help, but it does require some time and effort.
4. Cell Replacement: The chlorinator cell typically lasts 3-7 years, depending on usage and maintenance. The cost of replacing cell depends on the model.
5. Water Testing: Regular water testing is crucial to ensure proper operation. Test kits are relatively inexpensive.
6. Professional Maintenance: While not always necessary, some owners choose to have their systems professionally serviced annually. This might cost amount for per visit.
For commercial or industrial systems, annual maintenance costs can be significantly higher, often running into thousands of dollars annually, depending on the size and complexity of the system.
Long-Term Cost Considerations:
When evaluating the cost of a chlorine generator electrolyzer system, it's important to consider the long-term savings:
1. Reduced Chemical Costs: Traditional chlorination methods can cost $300-$800 per year in chemicals for a residential pool. A chlorine generator system significantly reduces these costs.
2. Lower Labor Costs: The automated nature of these systems reduces the time and effort required for water treatment, which can lead to significant labor savings, especially in commercial applications.
3. Extended Equipment Life: Consistent water quality can help extend the life of pool equipment and surfaces, potentially leading to long-term savings.
4. Energy Efficiency: Some modern chlorine generator systems are designed to be highly energy-efficient, potentially offsetting their electricity consumption through savings in other areas.
While the initial investment in a chlorine generator electrolyzer system can be substantial, many users find that the long-term benefits and cost savings make it a worthwhile investment. For residential pool owners, the system often pays for itself within 2-3 years. For larger commercial or industrial applications, the return on investment can be even quicker, especially when factoring in reduced labor costs and improved water quality.
It's important to conduct a thorough cost-benefit analysis based on your specific situation, considering factors such as local electricity rates, chemical costs, and regulatory requirements. Consulting with a professional can help provide a more accurate estimate of both installation and long-term costs for your particular application.
If you are interested in the products of Xi'an Taijin New Energy & Materials Sci-Tech Co., Ltd., please contact yangbo@tjanode.com.
References:
1. World Health Organization. (2020). "Guidelines for Drinking-water Quality: Fourth Edition Incorporating the First and Second Addenda."
2. Timberlake, K. C. (2015). "Chemistry: An Introduction to General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry." Pearson.
3. American Chemistry Council. (2022). "Chlorine Chemistry Division."
4. U.S. Environmental Protection Agency. (2021). "Disinfection Byproducts in Drinking Water."
5. National Swimming Pool Foundation. (2022). "Pool & Spa Operator Handbook."
6. Water Quality and Health Council. (2023). "Chlorine Chemistry."
7. Journal of Environmental Management. (2019). "Comparative study of electrochemical chlorine production from seawater and brine."
8. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. (2020). "Salt Chlorinators for Swimming Pools: An Overview."
9. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. (2022). "Healthy Swimming."
10. American Water Works Association. (2021). "Water Chlorination and Chloramination Practices and Principles."
YOU MAY LIKE
Related Industry Knowledge
- How do Titanium Electrodes Work in Salt Chlorination?
- How Does a Chlorine Electrolysis Cell Operate?
- What is the Role of Naturally Occurring Chloride in the Disinfection Process Using Titanium Electrodes?
- How Do Titanium Electrodes Enhance Salt Chlorination in Pool Disinfection Systems?
- Can Titanium Electrodes Be Used with Saltwater Chlorinators?
- How Does a Chlorine Generator Electrolyzer Enhance Pool Maintenance?
- What Is a Chlorine Generator Electrolyzer and How Does It Operate?
- What Industries Benefit from Chlorine Generator Electrolyzers for On-Site Production?
- What Factors Should Be Considered When Selecting a Chlorine Generator Electrolyzer System?