- English
- French
- German
- Portuguese
- Spanish
- Russian
- Japanese
- Korean
- Arabic
- Greek
- German
- Turkish
- Italian
- Danish
- Romanian
- Indonesian
- Czech
- Afrikaans
- Swedish
- Polish
- Basque
- Catalan
- Esperanto
- Hindi
- Lao
- Albanian
- Amharic
- Armenian
- Azerbaijani
- Belarusian
- Bengali
- Bosnian
- Bulgarian
- Cebuano
- Chichewa
- Corsican
- Croatian
- Dutch
- Estonian
- Filipino
- Finnish
- Frisian
- Galician
- Georgian
- Gujarati
- Haitian
- Hausa
- Hawaiian
- Hebrew
- Hmong
- Hungarian
- Icelandic
- Igbo
- Javanese
- Kannada
- Kazakh
- Khmer
- Kurdish
- Kyrgyz
- Latin
- Latvian
- Lithuanian
- Luxembou..
- Macedonian
- Malagasy
- Malay
- Malayalam
- Maltese
- Maori
- Marathi
- Mongolian
- Burmese
- Nepali
- Norwegian
- Pashto
- Persian
- Punjabi
- Serbian
- Sesotho
- Sinhala
- Slovak
- Slovenian
- Somali
- Samoan
- Scots Gaelic
- Shona
- Sindhi
- Sundanese
- Swahili
- Tajik
- Tamil
- Telugu
- Thai
- Ukrainian
- Urdu
- Uzbek
- Vietnamese
- Welsh
- Xhosa
- Yiddish
- Yoruba
- Zulu
Cathodic protection is a technique used to safeguard metal structures or pipelines from corrosion. It works by intentionally making the structure the cathode of an electrochemical cell, thereby preventing the metal from corroding.
There are two primary types:
Galvanic Cathodic Protection: This method employs a sacrificial anode made of a more reactive metal (like zinc or magnesium) that is connected to the structure needing protection. The sacrificial anode corrodes instead of the protected metal, preserving the integrity of the structure.
Impressed Current Cathodic Protection: Here, an external power source, such as a rectifier, is used to provide a continuous electric current to the structure through inert anodes. This method is more controllable and suitable for larger structures or those requiring precise levels of protection.
Cathodic protection is commonly utilized in various industries, especially in pipelines, underground tanks, offshore platforms, and ships, to prevent corrosion and extend the lifespan of metallic structures.
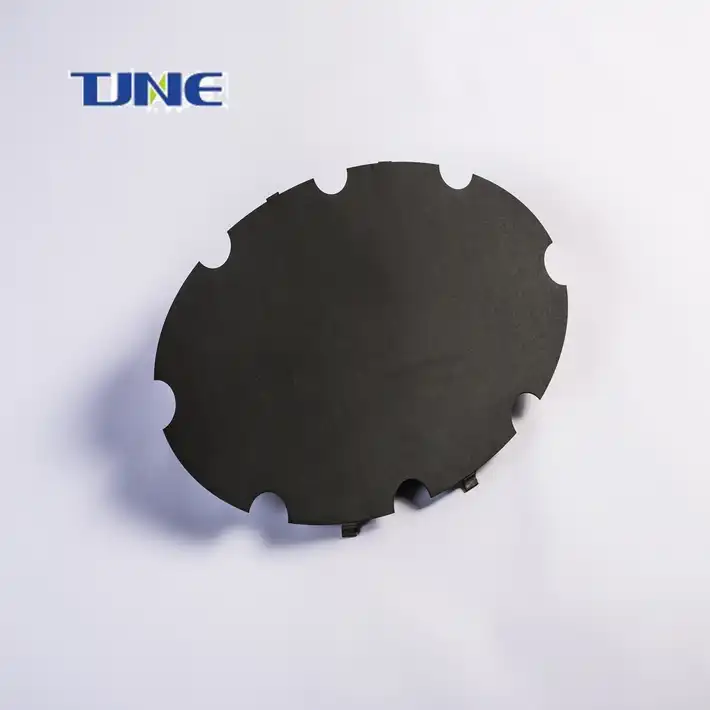
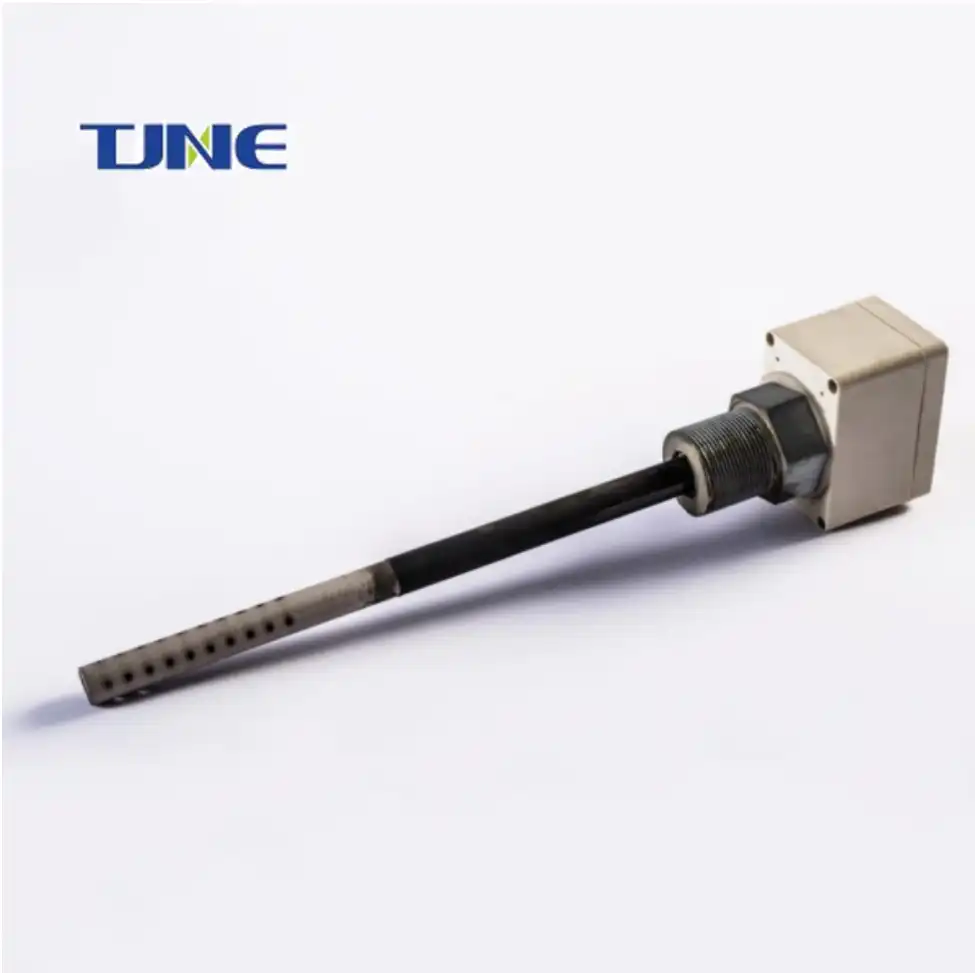
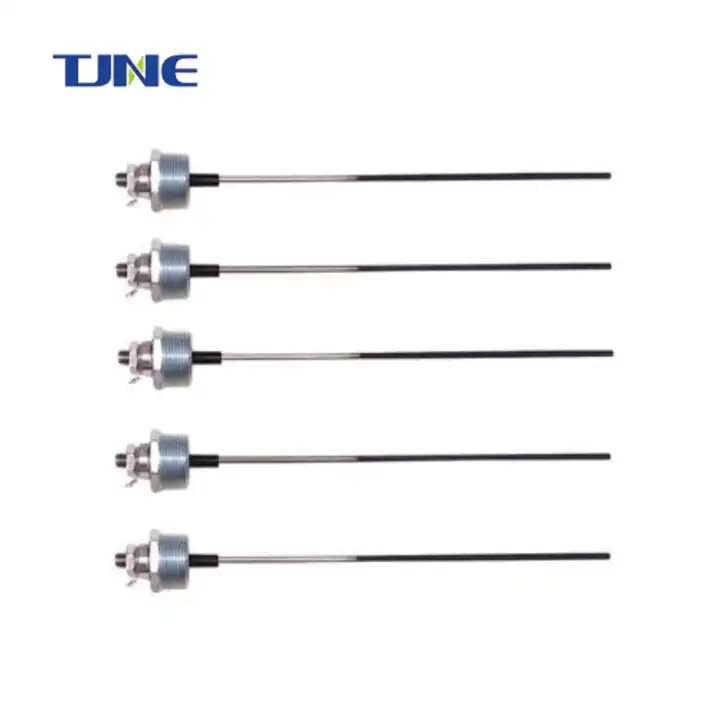
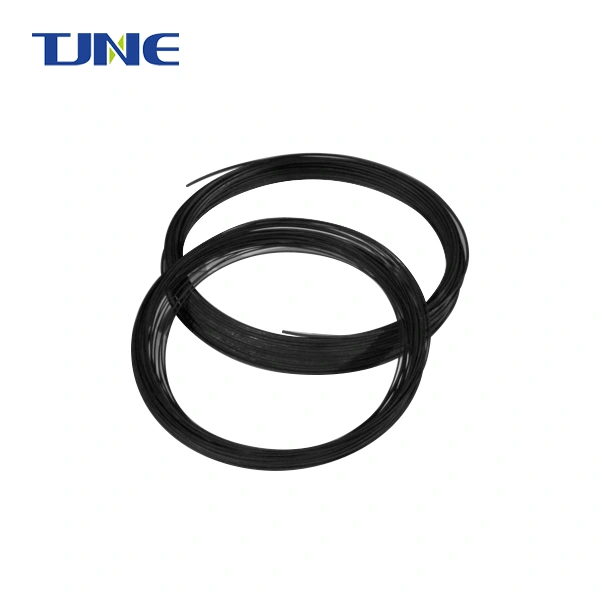
Cathodic protection include: mmo anode plate,electronic titanium anode rod,mmo titanium probe anode,mmo wire anode,mmo/ti flexible anode,mmo canister anode,mmo tubular taitanium anode,mmo ribbon anode,mmo titanium mesh anode,anode plate.