- English
- French
- German
- Portuguese
- Spanish
- Russian
- Japanese
- Korean
- Arabic
- Greek
- German
- Turkish
- Italian
- Danish
- Romanian
- Indonesian
- Czech
- Afrikaans
- Swedish
- Polish
- Basque
- Catalan
- Esperanto
- Hindi
- Lao
- Albanian
- Amharic
- Armenian
- Azerbaijani
- Belarusian
- Bengali
- Bosnian
- Bulgarian
- Cebuano
- Chichewa
- Corsican
- Croatian
- Dutch
- Estonian
- Filipino
- Finnish
- Frisian
- Galician
- Georgian
- Gujarati
- Haitian
- Hausa
- Hawaiian
- Hebrew
- Hmong
- Hungarian
- Icelandic
- Igbo
- Javanese
- Kannada
- Kazakh
- Khmer
- Kurdish
- Kyrgyz
- Latin
- Latvian
- Lithuanian
- Luxembou..
- Macedonian
- Malagasy
- Malay
- Malayalam
- Maltese
- Maori
- Marathi
- Mongolian
- Burmese
- Nepali
- Norwegian
- Pashto
- Persian
- Punjabi
- Serbian
- Sesotho
- Sinhala
- Slovak
- Slovenian
- Somali
- Samoan
- Scots Gaelic
- Shona
- Sindhi
- Sundanese
- Swahili
- Tajik
- Tamil
- Telugu
- Thai
- Ukrainian
- Urdu
- Uzbek
- Vietnamese
- Welsh
- Xhosa
- Yiddish
- Yoruba
- Zulu
Titanium electrodes play a crucial role in maintaining the pH balance of pool water, particularly in saltwater systems. These electrodes are essential components in the electrolysis process that generates chlorine from salt, helping to keep pool water clean and safe for swimmers. Understanding how titanium electrodes influence pH levels is vital for pool owners and maintenance professionals to ensure optimal water quality and swimmer comfort.
What are the benefits of using titanium electrodes in saltwater pool systems?
Titanium electrodes have become increasingly popular in saltwater pool systems due to their numerous advantages. These electrodes are integral to the chlorine generation process, which is the cornerstone of saltwater pool maintenance. Here's a closer look at the benefits of using titanium electrodes:
Corrosion Resistance: One of the primary advantages of titanium electrodes is their exceptional resistance to corrosion. Unlike other metals, titanium forms a protective oxide layer when exposed to oxygen, making it highly resistant to chemical attacks. This property is crucial in the harsh environment of saltwater pools, where the combination of salt, chlorine, and other chemicals can quickly degrade less durable materials.
Longevity: Thanks to their corrosion resistance, titanium electrodes have a significantly longer lifespan compared to electrodes made from other materials. This durability translates to reduced maintenance costs and fewer replacements over time, making titanium electrodes a cost-effective choice for pool owners in the long run.
Efficiency: Titanium electrodes are highly efficient in the chlorine generation process. They provide a stable surface for the electrolysis of salt, consistently producing the right amount of chlorine to keep the pool water clean and safe. This efficiency helps maintain a steady chlorine level, reducing the need for manual adjustments and chemical additions.
Minimal Impact on Water Chemistry: Titanium is an inert metal, meaning it doesn't react with or leach into the pool water. This property is crucial for maintaining the delicate balance of pool water chemistry. Unlike some other electrode materials that may introduce unwanted elements into the water, titanium electrodes help keep the water chemistry stable and predictable.
Environmentally Friendly: The use of titanium electrodes in saltwater systems contributes to a more environmentally friendly pool maintenance approach. By generating chlorine on-site through electrolysis, these systems reduce the need for transporting and storing potentially hazardous chlorine chemicals. Additionally, the longevity of titanium electrodes means fewer replacements and less waste over time.
Improved Swimmer Comfort: Saltwater pools using titanium electrodes often provide a more comfortable swimming experience. The chlorine levels produced by these systems tend to be more consistent and less harsh than those in traditional chlorine pools. This can result in reduced eye and skin irritation for swimmers, as well as a softer feel to the water.
Compatibility with Automation: Titanium electrodes work well with modern pool automation systems. Their stable performance allows for precise control of chlorine generation, which can be easily integrated into automated pool management systems. This compatibility enhances the overall efficiency of pool maintenance and can lead to better water quality management.
In summary, the benefits of using titanium electrodes in saltwater pool systems extend beyond their direct impact on water chemistry. They contribute to a more efficient, cost-effective, and swimmer-friendly pool environment, making them an excellent choice for both residential and commercial pool applications.
How does the Intex saltwater system maintain proper pH levels?
The Intex saltwater system, which utilizes titanium electrodes, plays a crucial role in maintaining proper pH levels in pool water. Understanding how this system works is essential for pool owners to ensure optimal water quality and swimmer comfort. Let's delve into the mechanics of the Intex saltwater system and its impact on pH balance:
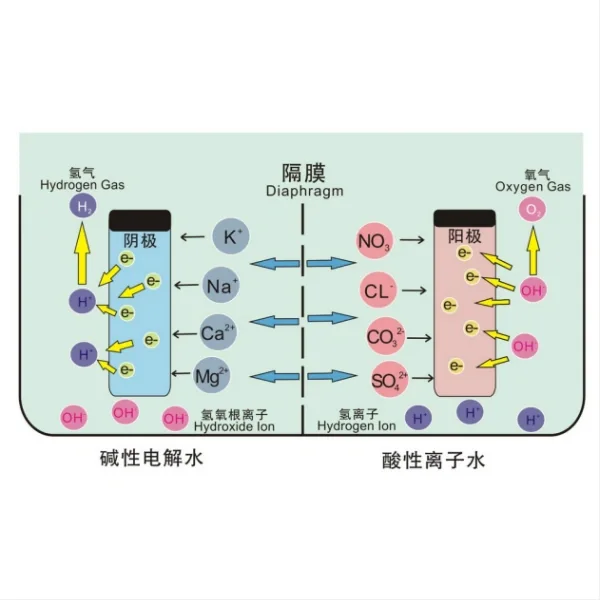
Electrolysis Process: At the heart of the Intex saltwater system is the electrolysis process. This system uses titanium electrodes to convert dissolved salt (sodium chloride) in the water into chlorine. When an electric current passes through the saltwater solution, it triggers a chemical reaction that produces hypochlorous acid (HOCl) and sodium hypochlorite (NaClO), which are effective sanitizing agents.
Chlorine Generation: The chlorine produced through this process helps to sanitize the pool water, eliminating harmful bacteria and algae. However, the generation of chlorine can have an impact on the pool's pH level. As chlorine is produced, it tends to increase the pH of the water slightly over time.
pH Buffering: To counteract the potential pH increase, the Intex saltwater system incorporates a buffering mechanism. This involves the production of a small amount of sodium hydroxide (NaOH) as a byproduct of the electrolysis process. Sodium hydroxide acts as a weak base, helping to stabilize the pH and prevent it from rising too quickly.
Automatic pH Control: Many Intex saltwater systems come with built-in pH sensors and control mechanisms. These sensors continuously monitor the pH level of the pool water. When the pH starts to drift outside the ideal range (typically 7.2 to 7.6), the system can automatically adjust the chlorine production rate or activate additional pH balancing features to bring the levels back into the optimal range.
Reverse Polarity: Intex saltwater systems often incorporate a reverse polarity feature. This periodically reverses the electric current flowing through the titanium electrodes. The reverse polarity helps to prevent scale buildup on the electrodes, which can affect their efficiency and, consequently, the system's ability to maintain proper pH levels.
Integration with Pool Chemistry: The Intex system works in conjunction with the pool's overall chemical balance. While it helps maintain chlorine levels and contributes to pH stability, it's designed to work alongside other chemical factors in the pool water. This includes alkalinity and calcium hardness, which also play roles in pH stability.
User Controls: Most Intex saltwater systems allow pool owners to adjust settings based on pool size, usage, and local conditions. These controls enable fine-tuning of chlorine production and, indirectly, pH management. Some advanced models may even allow for direct pH adjustment settings.
Continuous Circulation: The Intex system relies on proper water circulation to function effectively. Continuous circulation ensures that all pool water passes through the salt cell regularly, allowing for consistent chlorine production and pH management throughout the entire pool.
Monitoring and Maintenance: While the Intex saltwater system automates much of the pH management process, regular monitoring is still important. Pool owners should periodically test their water chemistry, including pH levels, to ensure the system is functioning correctly and to make any necessary manual adjustments.
Balanced Water Approach: The Intex system contributes to what is known as the "balanced water approach." This holistic view of pool chemistry considers how various factors, including pH, alkalinity, and calcium hardness, interact. By maintaining proper chlorine levels and contributing to pH stability, the Intex system plays a key role in this balanced approach.
In conclusion, the Intex saltwater system, with its titanium electrodes, maintains proper pH levels through a combination of controlled chlorine generation, buffering mechanisms, and automated monitoring and adjustment features. While it significantly reduces the need for manual pH management, it's important for pool owners to understand the system's operation and to perform regular checks to ensure optimal performance and water quality.

Can titanium electrodes in saltwater systems cause pH fluctuations?
While titanium electrodes in saltwater systems like the Intex are generally effective at maintaining stable pH levels, they can potentially contribute to pH fluctuations under certain conditions. Understanding these potential issues is crucial for pool owners to ensure optimal water quality and system performance. Let's explore the various factors that can lead to pH fluctuations in systems using titanium electrodes:
Electrode Efficiency: The efficiency of titanium electrodes can decrease over time due to scale buildup or wear. As the electrodes become less efficient, they may produce an imbalanced ratio of chlorine to sodium hydroxide, potentially leading to pH fluctuations. Regular cleaning and maintenance of the electrodes are essential to prevent this issue.
Water Chemistry Imbalances: If other aspects of pool water chemistry, such as alkalinity or calcium hardness, are out of balance, it can make it more difficult for the saltwater system to maintain a stable pH. These imbalances can cause the pH to fluctuate more readily, even with the buffering effects of the titanium electrode system.
High Chlorine Demand: During periods of heavy pool use or after significant rainfall, the chlorine demand may increase substantially. If the saltwater system struggles to keep up with this demand, it may lead to pH fluctuations as the system works harder to produce more chlorine.
Improper System Sizing: If a saltwater system with titanium electrodes is not properly sized for the pool volume, it may struggle to maintain consistent chlorine levels and pH balance. An undersized system may lead to pH fluctuations as it cycles on and off more frequently to meet the pool's needs.
Environmental Factors: External factors such as sunlight, temperature, and organic matter can affect the chlorine levels in the pool. These fluctuations in chlorine can indirectly impact pH levels, potentially causing them to vary more than usual.
Reverse Polarity Cycles: While the reverse polarity feature of many saltwater systems helps prevent scale buildup, the switching process can temporarily affect chlorine production and, consequently, pH levels. These fluctuations are usually minor but may be noticeable in some cases.
Water Source: The quality and chemical composition of the water used to fill and top up the pool can affect pH stability. Water with high mineral content or extreme pH levels can challenge the saltwater system's ability to maintain consistent pH levels.
System Settings: Incorrect settings on the saltwater system, such as improper chlorine production rates or pH target ranges, can lead to unnecessary pH fluctuations. It's important to calibrate the system correctly based on pool size, usage, and local conditions.
Electrode Material Quality: While titanium electrodes are generally very stable, the quality of the titanium and any coatings used can affect their performance. Lower-quality electrodes may be more prone to wear or inconsistent performance, potentially leading to pH fluctuations.

Interaction with Other Pool Equipment: The operation of other pool equipment, such as heaters, pumps, or UV systems, can sometimes interfere with the saltwater system's ability to maintain stable pH levels. Ensuring proper integration of all pool systems is crucial for maintaining consistent water chemistry.
User Behavior: Frequent addition of chemicals, inconsistent pool usage patterns, or improper maintenance practices can challenge the saltwater system's ability to maintain stable pH levels. Educating pool owners on proper pool care is essential for minimizing pH fluctuations.
System Age: As saltwater systems age, their ability to maintain consistent chlorine production and pH levels may diminish. Regular system checks and timely replacement of components, including electrodes, are necessary to ensure ongoing stability.
To mitigate these potential causes of pH fluctuations:
1. Regularly test and balance pool water chemistry.
2. Perform routine maintenance on the saltwater system, including cleaning the electrodes.
3. Ensure proper sizing and settings for the saltwater system.
4. Monitor and adjust for environmental factors and pool usage patterns.
5. Use high-quality water for filling and topping up the pool.
6. Integrate all pool systems properly to work in harmony.
7. Educate pool owners on best practices for pool maintenance.
8. Consider professional servicing for older systems or persistent issues.
By understanding these potential causes of pH fluctuations and taking proactive measures, pool owners can maximize the benefits of titanium electrodes in their saltwater systems and maintain stable, comfortable pool water for swimmers.
In conclusion, titanium electrodes play a vital role in maintaining the pH balance of pool water, especially in saltwater systems. Their corrosion resistance, efficiency, and longevity make them an excellent choice for chlorine generation and pH management. While the Intex saltwater system, utilizing titanium electrodes, is designed to maintain proper pH levels automatically, it's important to understand that various factors can still influence pH stability. Regular monitoring, proper maintenance, and an understanding of pool water chemistry are essential for ensuring that titanium electrodes continue to effectively contribute to a balanced and comfortable swimming environment.
If you are interested in the products of Xi'an Taijin New Energy & Materials Sci-Tech Co., Ltd., please contact yangbo@tjanode.com.
References:
1. Lowry, R. (2021). The Complete Pool Manual for Homeowners and Professionals: A Step-by-Step Maintenance Guide. Storey Publishing, LLC.
2. Tamminen, T. (2019). The Ultimate Guide to Pool Maintenance. McGraw Hill Professional.
3. Wolfe, J. (2018). Chemistry of Swimming Pool Maintenance. Journal of Chemical Education, 95(10), 1714-1720.
4. Intex Recreation Corp. (2023). Intex Saltwater System Manual.
5. Bauer, R. (2020). Electrochemistry of Swimming Pool Water Treatment. Electrochimica Acta, 337, 135785.
6. Wojtowicz, J. A. (2017). Swimming Pool Water Balance. Journal of the Swimming Pool and Spa Industry, 2(1), 20-34.
7. Lenntech B.V. (2022). Titanium Electrodes in Water Treatment.
8. American Chemistry Council. (2023). Pool Chemical Safety.
9. World Health Organization. (2021). Guidelines for Safe Recreational Water Environments: Volume 2, Swimming Pools and Similar Environments. WHO Press.
10. Zhao, Q., Zhang, J., & Wang, W. (2020). Recent Advances in Electrochemical Technologies for Swimming Pool Water Treatment. Water Research, 184, 116170.
Related Industry Knowledge
- How Long Do Titanium Anodes Last in a Swimming Pool System?
- How to Install Titanium Anodes in Your Swimming Pool?
- What are the Guidelines and Regulations for Swimming Pool Disinfection?
- How Long Do Titanium Electrodes Last in Swimming Pool Applications?
- How do Titanium Electrodes Contribute to Sustainable Swimming?
- What is a Titanium Electrode for Swimming Pool Disinfection?
- Are There Any Safety Considerations When Using Titanium Electrodes in Swimming Pools?