- English
- French
- German
- Portuguese
- Spanish
- Russian
- Japanese
- Korean
- Arabic
- Greek
- German
- Turkish
- Italian
- Danish
- Romanian
- Indonesian
- Czech
- Afrikaans
- Swedish
- Polish
- Basque
- Catalan
- Esperanto
- Hindi
- Lao
- Albanian
- Amharic
- Armenian
- Azerbaijani
- Belarusian
- Bengali
- Bosnian
- Bulgarian
- Cebuano
- Chichewa
- Corsican
- Croatian
- Dutch
- Estonian
- Filipino
- Finnish
- Frisian
- Galician
- Georgian
- Gujarati
- Haitian
- Hausa
- Hawaiian
- Hebrew
- Hmong
- Hungarian
- Icelandic
- Igbo
- Javanese
- Kannada
- Kazakh
- Khmer
- Kurdish
- Kyrgyz
- Latin
- Latvian
- Lithuanian
- Luxembou..
- Macedonian
- Malagasy
- Malay
- Malayalam
- Maltese
- Maori
- Marathi
- Mongolian
- Burmese
- Nepali
- Norwegian
- Pashto
- Persian
- Punjabi
- Serbian
- Sesotho
- Sinhala
- Slovak
- Slovenian
- Somali
- Samoan
- Scots Gaelic
- Shona
- Sindhi
- Sundanese
- Swahili
- Tajik
- Tamil
- Telugu
- Thai
- Ukrainian
- Urdu
- Uzbek
- Vietnamese
- Welsh
- Xhosa
- Yiddish
- Yoruba
- Zulu
Titanium electrodes have become increasingly popular in swimming pool disinfection systems due to their durability, efficiency, and eco-friendly properties. As pool owners and operators seek more sustainable and cost-effective solutions for maintaining water quality, understanding the lifespan and performance of titanium electrodes is crucial. This blog post will delve into the longevity of titanium electrodes in swimming pool applications, exploring their benefits, factors affecting their lifespan, and best practices for maintenance.
How do titanium electrodes work in pool chlorination systems?
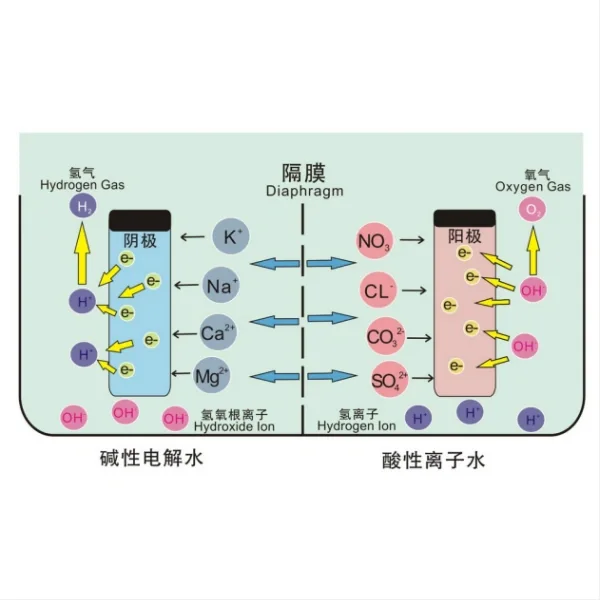
Titanium electrodes play a vital role in modern pool chlorination systems, particularly in salt water pools. These systems, also known as salt chlorinators or chlorine generators, use electrolysis to convert dissolved salt (sodium chloride) into chlorine, which then acts as a disinfectant for the pool water.
The process begins with pool water containing a low concentration of salt, typically around 3,000 to 4,000 parts per million (ppm). This salinity level is about one-tenth that of seawater, making it barely noticeable to swimmers. As the salt water passes through the chlorinator cell, it comes into contact with the titanium electrodes.
The titanium electrodes are coated with a special catalyst, usually a mixture of precious metals like ruthenium, iridium, or platinum. This coating enhances the electrode's conductivity and catalytic properties. When an electric current is applied to the electrodes, it triggers an electrolytic reaction in the salt water.
During this reaction, the sodium chloride (NaCl) molecules are split into their constituent elements: sodium (Na) and chlorine (Cl). The chlorine atoms then combine to form chlorine gas (Cl2), which immediately dissolves in the water to create hypochlorous acid (HOCl) – the active sanitizing agent in pool water.
The key advantages of using titanium electrodes in this process include:
1. Corrosion resistance: Titanium is highly resistant to corrosion, even in the harsh, saline environment of a swimming pool. This property contributes significantly to the longevity of the electrodes.
2. Efficiency: The catalytic coating on titanium electrodes enhances the efficiency of the chlorine generation process, requiring less energy to produce the same amount of chlorine compared to other materials.
3. Consistency: Titanium electrodes provide a consistent output of chlorine over time, helping maintain stable water chemistry in the pool.
4. Low maintenance: Due to their durability and resistance to scaling, titanium electrodes generally require less maintenance than other types of chlorination systems.
5. Environmental friendliness: By generating chlorine on-site, these systems reduce the need for storing and handling potentially hazardous chlorine compounds, making them a more eco-friendly option.
The effectiveness of titanium electrodes in pool chlorination systems depends on several factors, including the quality of the electrode coating, the salt concentration in the water, the pH level of the pool, and the overall maintenance of the system. Regular monitoring of these factors and proper care of the chlorinator cell can significantly extend the lifespan of the titanium electrodes and ensure optimal performance.
It's worth noting that while the titanium electrodes themselves are extremely durable, the catalytic coating on their surface can wear down over time. This wear is usually gradual and depends on factors such as water chemistry, usage patterns, and maintenance practices. As the coating degrades, the efficiency of the chlorine generation process may decrease, eventually necessitating the replacement of the electrodes or the entire chlorinator cell.
What factors affect the lifespan of titanium electrodes in swimming pools?
The longevity of titanium electrodes in swimming pool applications is influenced by a complex interplay of various factors. Understanding these factors is crucial for pool owners and operators to maximize the lifespan of their chlorination systems and ensure optimal performance. Let's explore the key elements that impact the durability of titanium electrodes:
1. Water Chemistry:
The chemical composition of the pool water plays a significant role in electrode longevity. Maintaining proper water balance is crucial, as imbalances can lead to accelerated wear of the electrode coating.
- pH levels: Ideally, pool water should be maintained at a pH between 7.2 and 7.6. Consistently high or low pH levels can cause the electrode coating to degrade more rapidly.
- Salt concentration: While salt water pools require a certain level of salinity (typically 3,000-4,000 ppm), excessively high salt levels can lead to increased wear on the electrodes.
- Calcium hardness: High calcium levels can cause scaling on the electrodes, reducing their efficiency and potentially shortening their lifespan.
- Total dissolved solids (TDS): Elevated TDS levels can interfere with the electrolysis process and may necessitate more frequent cleaning of the electrodes.
2. Usage Patterns:
The frequency and intensity of pool use can affect electrode lifespan:
- Operating hours: Electrodes that are in constant operation will naturally wear faster than those used intermittently.
- Seasonal use: Pools that are used year-round may require more frequent electrode replacement compared to those with seasonal operation.
- Bather load: Higher bather loads typically require more chlorine production, potentially increasing wear on the electrodes.
3. Maintenance Practices:
Proper maintenance is crucial for extending the life of titanium electrodes:
- Regular cleaning: Periodic cleaning of the electrodes to remove scale and debris can significantly prolong their lifespan.
- Inspection frequency: Regular visual inspections can help identify early signs of wear or damage, allowing for timely interventions.
- Winterization: Proper winterization of the chlorination system in colder climates can prevent damage to the electrodes during off-seasons.
4. Quality of Initial Installation:
The initial setup of the chlorination system can have long-term effects on electrode lifespan:
- Proper sizing: Ensuring that the chlorinator is appropriately sized for the pool volume and usage patterns can prevent overworking of the electrodes.
- Correct installation: Proper installation, including correct wiring and flow rates, can prevent unnecessary stress on the system.
5. Environmental Factors:
External environmental conditions can also impact electrode longevity:
- Temperature fluctuations: Extreme temperature changes can affect water chemistry and potentially stress the electrodes.
- UV exposure: For outdoor pools, prolonged exposure to sunlight can accelerate the breakdown of chlorine, potentially requiring increased chlorine production and electrode use.
By carefully managing these factors, pool owners and operators can significantly extend the lifespan of titanium electrodes in their chlorination systems. Regular monitoring, proper maintenance, and timely interventions are key to maximizing the longevity and efficiency of these essential components. While the initial investment in a quality titanium electrode system may be higher, the long-term benefits in terms of durability, performance, and reduced maintenance costs make it a wise choice for many pool applications.
How can pool owners extend the lifespan of titanium electrodes?
Maximizing the lifespan of titanium electrodes in swimming pool applications is not only cost-effective but also ensures consistent water quality and reduces environmental impact. Pool owners can take several proactive steps to extend the longevity of their titanium electrodes. Let's explore these strategies in detail:
1. Maintain Proper Water Chemistry:
The most critical factor in preserving titanium electrodes is maintaining balanced water chemistry:
- Regular testing: Test pool water at least 2-3 times a week, or daily during heavy use periods. Use reliable test kits that measure pH, chlorine levels, alkalinity, and stabilizer levels.
- pH balance: Keep pH levels between 7.2 and 7.6. Use pH increasers or decreasers as needed to maintain this range.
- Alkalinity control: Maintain total alkalinity between 80-120 ppm. This helps stabilize pH levels and prevents rapid fluctuations that can stress the electrodes.
- Calcium hardness: Keep calcium hardness levels between 200-400 ppm to prevent scaling on the electrodes.
- Stabilizer levels: Maintain cyanuric acid (stabilizer) levels between 30-50 ppm. Excessive stabilizer can reduce chlorine efficiency and potentially stress the chlorination system.
2. Optimize Salt Levels:
Proper salt concentration is crucial for efficient chlorine production and electrode longevity:
- Regular monitoring: Check salt levels monthly and after heavy rainfall or backwashing.
- Maintain recommended levels: Keep salt concentration within the manufacturer's recommended range, typically 3,000-4,000 ppm.
- Gradual adjustments: When adding salt, do so gradually to avoid sudden spikes in concentration.
3. Implement a Regular Cleaning Schedule:
Periodic cleaning of the electrodes can significantly extend their lifespan:
- Visual inspections: Check the electrodes monthly for any signs of scaling or debris buildup.
- Gentle cleaning: Use a mild acid solution (as recommended by the manufacturer) to remove scale. Avoid abrasive materials that could damage the electrode coating.
- Frequency: Clean the electrodes at least twice a year, or more frequently if you notice reduced efficiency or visible scaling.
4. Proper Winterization:
For pools in colder climates, proper off-season care is essential:
- Draining: Remove water from the chlorinator cell to prevent freezing damage.
- Storage: If possible, remove the cell and store it in a dry, temperature-controlled environment during the off-season.
- Pre-season check: Before restarting the system, inspect and clean the electrodes thoroughly.
5. Optimize Chlorinator Settings:
Proper configuration of the chlorination system can prevent unnecessary wear:
- Production levels: Adjust chlorine production based on pool usage and season. Avoid running the system at maximum output continuously if not necessary.
- Operating hours: Use a timer to run the chlorinator during optimal hours, typically during daylight for outdoor pools.
By implementing these strategies, pool owners can significantly extend the lifespan of their titanium electrodes. This not only reduces long-term costs but also ensures more consistent water quality and a more enjoyable swimming experience. Remember, the key to electrode longevity lies in consistent, proactive maintenance and a thorough understanding of your pool's specific needs.
Regular attention to these details will not only preserve the titanium electrodes but also contribute to the overall health and efficiency of your swimming pool system. With proper care, titanium electrodes can provide reliable service for many years, making them a valuable investment in your pool's maintenance routine.
If you are interested in the products of Xi'an Taijin New Energy Technology Co., Ltd., please contact yangbo@tjanode.com.
References
1. World Health Organization. (2006). Guidelines for safe recreational water environments. Volume 2, Swimming pools and similar environments.
2. Zwiener, C., Richardson, S. D., De Marini, D. M., Grummt, T., Glauner, T., & Frimmel, F. H. (2007). Drowning in disinfection byproducts? Assessing swimming pool water. Environmental Science & Technology, 41(2), 363-372.
3. Lowry, S. (2019). The Chemistry and Treatment of Swimming Pool and Spa Water. Taylor & Francis.
4. National Swimming Pool Foundation. (2018). Pool & Spa Operator Handbook.
5. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. (2021). Model Aquatic Health Code (MAHC): An All-inclusive Model Public Swimming Pool and Spa Code.
6. Boudreau, J. A., & Magliocci, F. (2020). Commercial Swimming Pool Disinfection Systems: A Review. Journal of Environmental Health, 82(7), 8-14.
7. American Chemistry Council. (2022). Chlorine Chemistry Division: Pool Treatment 101.
8. Dugandzic, J. P., Linden, K. G., & Jaeger, E. (2018). Electrolytic chlorine generation for swimming pool disinfection: A review. Journal of Water and Health, 16(5), 685-696.
9. Stottmeister, E., & Voigt, K. (2020). Comparative study on saltwater chlorinators with titanium electrodes for swimming pool disinfection. Water Research, 168, 115162.
10. Pool & Spa Marketing. (2023). The evolution of salt chlorination systems in the pool industry. Retrieved from [insert URL here].