- English
- French
- German
- Portuguese
- Spanish
- Russian
- Japanese
- Korean
- Arabic
- Greek
- German
- Turkish
- Italian
- Danish
- Romanian
- Indonesian
- Czech
- Afrikaans
- Swedish
- Polish
- Basque
- Catalan
- Esperanto
- Hindi
- Lao
- Albanian
- Amharic
- Armenian
- Azerbaijani
- Belarusian
- Bengali
- Bosnian
- Bulgarian
- Cebuano
- Chichewa
- Corsican
- Croatian
- Dutch
- Estonian
- Filipino
- Finnish
- Frisian
- Galician
- Georgian
- Gujarati
- Haitian
- Hausa
- Hawaiian
- Hebrew
- Hmong
- Hungarian
- Icelandic
- Igbo
- Javanese
- Kannada
- Kazakh
- Khmer
- Kurdish
- Kyrgyz
- Latin
- Latvian
- Lithuanian
- Luxembou..
- Macedonian
- Malagasy
- Malay
- Malayalam
- Maltese
- Maori
- Marathi
- Mongolian
- Burmese
- Nepali
- Norwegian
- Pashto
- Persian
- Punjabi
- Serbian
- Sesotho
- Sinhala
- Slovak
- Slovenian
- Somali
- Samoan
- Scots Gaelic
- Shona
- Sindhi
- Sundanese
- Swahili
- Tajik
- Tamil
- Telugu
- Thai
- Ukrainian
- Urdu
- Uzbek
- Vietnamese
- Welsh
- Xhosa
- Yiddish
- Yoruba
- Zulu
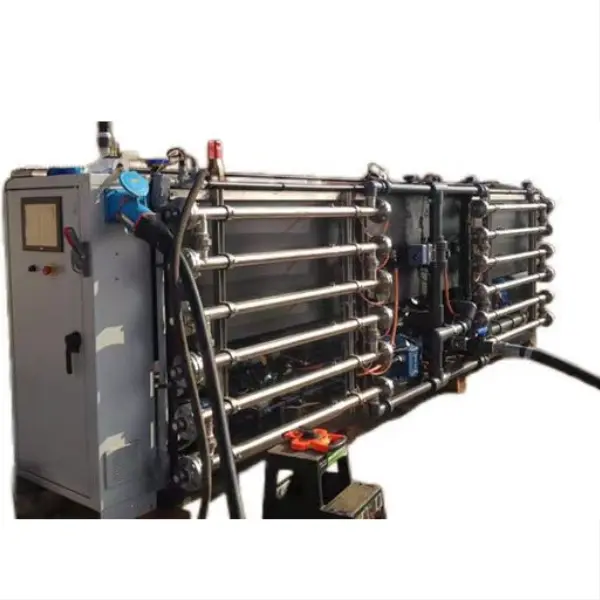
The use of titanium anodes in zinc electrowinning processes has gained significant attention in recent years due to its potential cost-effectiveness and improved performance. This innovative approach combines the durability and conductivity of titanium with the property of mixed metal oxide coating, offering a promising solution for industries seeking to optimize their zinc electrowinning operations. In this blog post, we'll explore the cost-effectiveness of using titanium anoodes in zinc electrowinning and address some key questions related to this technology.
How do titanium anodes compare to traditional anoodes in zinc electrowinning?
Titanium anodes have emerged as a superior alternative to traditional anodes in zinc electrowinning processes, offering several advantages that contribute to their growing popularity. The primary benefit of titanium anodes lies in their exceptional corrosion resistance, which significantly extends their lifespan compared to conventional materials such as lead or graphite. This durability translates to reduced replacement costs and less frequent production downtime, ultimately improving the overall efficiency of zinc electrowinning operations.
Another crucial advantage of titanium anodes is their high electrical conductivity. This property allows for more efficient current distribution across the anode surface, resulting in more uniform and improved quality of zinc electrowinning. The superior conductivity also means that titanium anodes can operate at lower voltages, potentially reducing energy consumption and associated costs.
Furthermore, titanium anodes exhibit excellent dimensional stability, maintaining their shape and size even under harsh plating conditions. This stability ensures consistent performance over time, leading to more predictable and reliable electrowinning results. In contrast, traditional anodes may deform or erode over time, causing variations in the electrowinning process and potentially compromising product quality.
The environmental impact of titanium anodes is also worth considering. Unlike lead anodes, which can pose significant environmental and health risks, titanium is a non-toxic material that aligns well with increasing environmental regulations and sustainability goals in the electrowinning industry.
However, it's important to note that the initial cost of titanium anodes is generally higher than that of traditional materials. This upfront investment can be a barrier for some companies, particularly smaller operations with limited capital. Nevertheless, the long-term benefits often outweigh the initial costs, making titanium anodes a cost-effective choice for many electrowinning businesses.

In terms of performance, titanium electrodes have demonstrated superior current efficiency in zinc electrowinning processes. This increased efficiency means that a higher percentage of the electrical current is utilized for the actual zinc electrowinning, reducing waste and improving the overall economics of the electrowinning operation.
What factors influence the cost-effectiveness of titanium anodes?
Several factors play a crucial role in determining the cost-effectiveness of titanium anodes in zinc electrowinning applications. Understanding these factors is essential for businesses considering the adoption of this technology.
Firstly, the quality of the mixed metal oxide coating significantly impacts the performance and longevity of the titanium anodes. A uniform and adherent coating on the titanium substrate enhances its corrosion resistance and conductivity. This improved quality directly translates to longer anode life and more consistent electrowinning results, both of which contribute to cost-effectiveness.
The composition of the coating is another critical factor. Different coatings, such as PbO2 or mixed metal oxides, can be applied to the titanium substrate to optimize its properties for zinc electrowinning. The choice of coating material affects not only the initial cost but also the long-term performance and durability of the anode.
Operational parameters, including current density, temperature, and electrolyte composition, also influence the cost-effectiveness of titanium anodes. Optimizing these parameters can lead to improved energy efficiency, reduced waste, and enhanced electrowinning quality. For instance, operating at the optimal current density can maximize zinc electrowinning rates while minimizing side reactions that waste energy and materials.

The scale of the electrowinning operation is another important consideration. Larger operations may benefit more from the use of titanium anodes due to economies of scale. The higher initial investment can be more easily justified when spread across a larger production volume, and the benefits of improved efficiency and reduced downtime become more pronounced.
Maintenance practices also play a role in the cost-effectiveness of these anodes. Proper care and regular maintenance can significantly extend the lifespan of titanium anodes, maximizing their value over time. This includes routine cleaning, inspection for damage, and timely replacement of worn components.
The specific requirements of the zinc electrowinning application must also be considered. Some applications may demand higher purity or more precise control over the electrowinning process, which can influence the choice of anode material and coating. In these cases, the superior performance of titanium anodes may justify their higher cost.
Lastly, the availability of skilled personnel to operate and maintain the electrowinning equipment can impact cost-effectiveness. Proper training and expertise are essential to fully leverage the benefits of titanium anodes and ensure their optimal performance over time.
How can businesses optimize the use of titanium anodes in their zinc electrowinning processes?
Optimizing the use of titanium anodes in zinc electrowinning processes is crucial for businesses looking to maximize their cost-effectiveness and overall performance. There are several strategies and best practices that companies can implement to achieve this goal.
First and foremost, conducting a thorough analysis of the specific zinc electrowinning requirements is essential. This involves evaluating factors such as the desired zinc quality, required production volume, and quality standards. By understanding these parameters, businesses can select the most appropriate titanium anode configuration and coating composition to meet their needs efficiently.
Implementing advanced process control systems can significantly enhance the performance of titanium anodes in zinc electrowinning. These systems can monitor and adjust key parameters such as current density, temperature, and electrolyte composition in real-time, ensuring optimal operating conditions are maintained. This level of control not only improves electrowinning quality but also extends the lifespan of the anodes by preventing excessive wear or degradation.

Regular maintenance and cleaning of titanium electrodes are critical for maintaining their efficiency over time. Developing a comprehensive maintenance schedule that includes routine inspections, cleaning procedures, and timely replacement of worn components can prevent unexpected failures and ensure consistent performance. Training operators in proper handling and maintenance techniques is also crucial for maximizing the longevity of these anodes.
Optimizing the electrolyte composition is another key aspect of improving the cost-effectiveness of titanium anodes in zinc electrowinning. This may involve fine-tuning the concentration of zinc ions, adjusting pH levels, or incorporating additives that enhance electrowinning efficiency and quality. Regularly monitoring and replenishing the electrolyte can help maintain optimal conditions for the anodes to function at their best.
Businesses should also consider implementing energy-efficient practices in their zinc electrowinning operations. Additionally, optimizing the layout of the electrowinning line to minimize current losses and improve current distribution can enhance overall efficiency.
Investing in research and development efforts to continuously improve anode design and coating technologies can yield long-term benefits. This may involve collaborating with anode manufacturers or academic institutions to develop customized solutions that address specific challenges in the zinc electrowinning process.
Implementing quality control measures throughout the electrowinning process is essential for ensuring consistent results and minimizing waste. This includes regular testing of zinc products, monitoring of electrode performance, and tracking of key performance indicators such as current efficiency and energy consumption.
Finally, businesses should stay informed about the latest developments in titanium anode technology and zinc electrowinning techniques. Attending industry conferences, participating in workshops, and engaging with suppliers like Xi'an Taijin New Energy & Materials Sci-Tech Co., Ltd can provide valuable insights into emerging trends and best practices.
By implementing these strategies, businesses can optimize their use of titanium electrodes in zinc electrowinning processes, ultimately improving cost-effectiveness, product quality, and operational efficiency.
In conclusion, the cost-effectiveness of using titanium anodes in zinc electrowinning is influenced by a complex interplay of factors, including initial investment, long-term performance, operational efficiency, and specific application requirements. While the upfront costs may be higher compared to traditional anodes, the potential for improved electrowinning quality, reduced downtime, and lower operational costs over time make titanium anodes an attractive option for many businesses. By carefully considering the factors discussed in this blog post and implementing optimization strategies, companies can make informed decisions about incorporating electrodeposited titanium anodes into their zinc electrowinning processes, potentially realizing significant benefits in terms of cost-effectiveness and overall performance.
If you are interested in the products of Xi'an Taijin New Energy & Materials Sci-Tech Co., Ltd., please contact yangbo@tjanode.com.
References:
1. Zhang, Y., et al. (2022). "Advances in titanium-based electrodes for electrochemical applications." Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 10(15), 8012-8038.
2. Walsh, F. C., & Ponce de León, C. (2018). "Progress in electrochemical engineering through developments in electrode materials and design." Electrochimica Acta, 280, 121-148.
3. Gamburg, Y. D., & Zangari, G. (2019). "Theory and practice of metal electrodeposition." Springer Science & Business Media.
4. Schlesinger, M., & Paunovic, M. (Eds.). (2011). "Modern electroplating" (Vol. 55). John Wiley & Sons.
5. Santana, R. A. C., et al. (2020). "Electrodeposition of zinc from alkaline solution containing additives." Journal of Applied Electrochemistry, 50(4), 483-497.
6. Gabe, D. R. (1997). "The role of hydrogen in metal electrodeposition processes." Journal of Applied Electrochemistry, 27(8), 908-915.
7. Dini, J. W., & Snyder, D. D. (2010). "Electrodeposition of zinc." Modern Electroplating, 5, 423-460.
8. Popov, K. I., et al. (2016). "Fundamental aspects of electrometallurgy." Springer.
9. Lou, H. H., & Huang, Y. (2006). "Electroplating." Encyclopedia of Chemical Processing, 1-10.
10. Walsh, F. C., & Low, C. T. J. (2016). "A review of developments in the electrodeposition of tin." Surface and Coatings Technology, 288, 79-94.
Related Industry Knowledge
- How do Ruthenium Iridium Coated Titanium Anodes Impact Metal Electrowinning?
- How Do Electrodeposited Titanium Electrodes Transform Zinc Electrodeposition Processes for Sustainability and Efficiency?
- How Do Titanium Anodes Enhance Zinc Electrowinning Processes?
- What are the Environmental Benefits of Using Titanium Electrodes for Cobalt Electrowinning?
- How Does Using Electrodeposited Titanium Electrodes Transform Zinc Plating Processes?
- Can Titanium Anodes Revolutionize Zinc Electrodeposition?